Radiographic Imaging in Pediatric Bone Fractures: Diagnosis and Clinical Challenges
14/11/2024 Views : 163
Faradilla Novita Anggreini
Bone fractures in children are a common condition that often occurs due to injury or trauma. The differences in the anatomy and physiology of children's bones compared to adults make the diagnosis and management of fractures more complex. One of the primary methods for diagnosing fractures in children is radiographic imaging (X-rays). This article will discuss the role of radiography in detecting bone fractures in children as well as the clinical challenges that may arise.
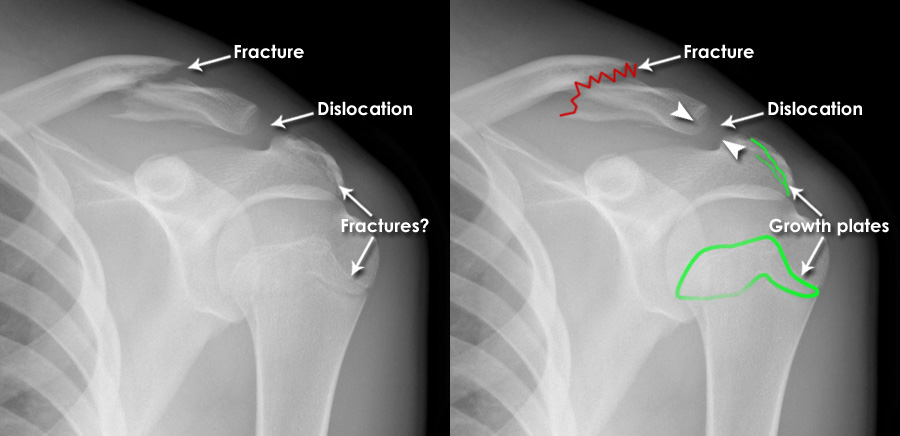
Conventional radiography is the first imaging modality used to assess fractures in children. This technique provides clear images of bone structures, helping in several aspects such as fracture identification, determining the type of fracture, and evaluating the healing process. Radiography can show fracture lines, soft tissue swelling, and bone displacement caused by trauma. Additionally, it helps in identifying typical fracture types in children, such as greenstick fractures, torus (buckle) fractures, and epiphyseal (Salter-Harris) fractures. Radiography is also used to monitor the bone healing process, including the formation of a callus, which indicates bone repair.
However, despite its usefulness, there are several challenges in using radiography for children. One of these challenges is the variation in bone growth. As children's bones are still in the growth phase, growth plates can resemble fractures, which may lead to misinterpretation. Additionally, certain fractures, such as stress fractures or those involving cartilage, can be difficult to detect with standard radiography. Another concern is radiation exposure; although the radiation dose in radiography is relatively low, it should still be carefully considered, especially in children, to reduce long-term risks.
Overall, radiographic imaging remains a primary diagnostic tool in detecting and monitoring bone fractures in children. However, interpreting radiographic results requires expertise to distinguish between actual fractures and normal anatomical variations. Therefore, collaboration between radiologists and orthopedic specialists is crucial to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal treatment planning for pediatric patients.
