Welfare Comparison of Informal Sector Workers Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic (Case Study: Denpasar City)
20/11/2021 Views : 292
Desak Putu Eka Nilakusmawati
The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted reducing working hours
and income in the informal sector caused by restrictions on activities and
movement of people to suppress the rate of increase in the number of positive
COVID-19 cases. How is the picture of the welfare of informal sector workers in
Denpasar during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to before? A survey of 150
respondents who are informal sector workers obtained interesting survey results
to study. The indicator of welfare, in this case, is the income of the
respondents.
Changes in respondent's income during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to before the pandemic, which was obtained from respondents' answers to the question item "In your opinion, how is your income during the COVID-19 pandemic when compared to your income before the COVID-19 pandemic?", with decreasing, fixed, increasing answer choice options. Results of respondents' answers that most of them 90 percent (135 respondents) stated that their income from working in the informal sector are decreased compared to before the pandemic, around 4.7 percent (7 respondents) said their income was fixed. The remaining 5.3 percent (8 respondents) stated that their income increased during the pandemic compared to pre-pandemic income.
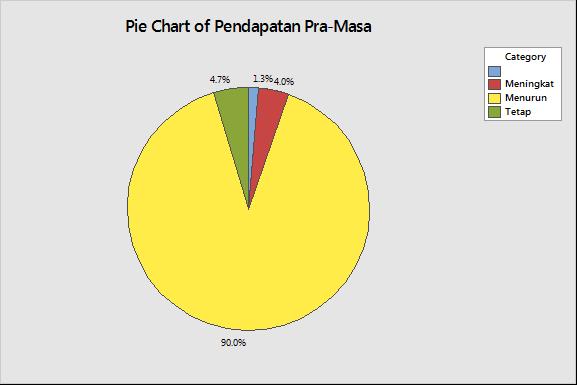
Figure 1. Changes in Respondents'
Income During the Pandemic Period compared to Before the COVID-19 Pandemic
However, when viewed as a whole, the respondent's income
data based on the survey results showed a decrease in the average income of
respondents during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to before the pandemic. The
average income of respondents before the pandemic was IDR 3,623,333.33 with a
minimum average income range of IDR 300,000 - and a maximum of IDR 26,000,000,
while the average income of respondents during the pandemic was IDR
2,342,666.67, with a minimum income of IDR 900,000, - and a maximum income of
IDR 13,000,000,-.
The correlation between the variables of average income before and during the pandemic was 0.922, with a significance of 0.000. According to the findings, the average income of respondents prior to and during the pandemic is significantly different. Similarly, the average working hours before and during the pandemic show a correlation value of 0.801 with a significance of 0.000, indicating that respondents' average working hours differ significantly between before and during the pandemic.
Paired sample T-test for the average income before and during the pandemic obtained the probability (Sig. 2 tailed) is 0.000, which means that the average income of respondents before the pandemic and during the pandemic is significantly different. Likewise, only the working hours of respondents before the pandemic had a significantly different average.
