Onion as a mean of testing the toxicity of environmental pollutants
18/01/2021 Views : 1514
Made Pharmawati
Environmental pollution has a
very broad impact on humans, animals, plants and other living things. Many
pollutants have an effect on human health. Pollutants can be synthetic or
natural materials. Industrial waste can contain heavy metals that pollute water
and soil, while the agricultural sector can cause insecticide residues in soil
and irrigation water.
Pollutant toxicity testing is
usually carried out using experimental animals because this test assumes that
animals are more sensitive than plants to chemical effects. In addition,
animals have a similar system to humans, so that they have good validity when
applied to humans. There are several obstacles in using animals as toxicity
bioassays, for example it takes a long time and is expensive. The toxicity of a
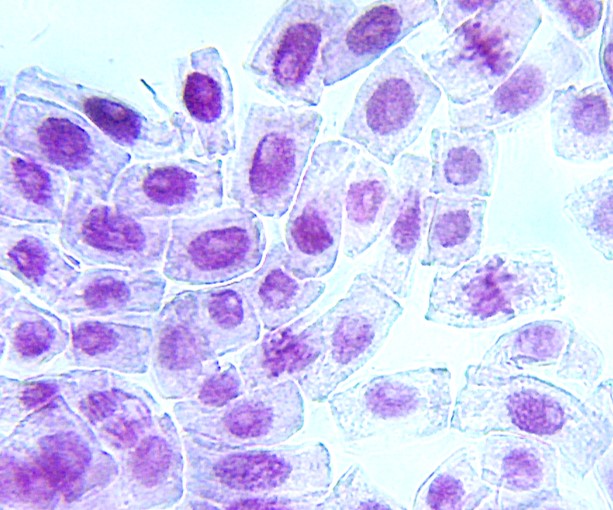
substance can be observed through chromosomal damage caused by a compound.
Observation of chromosomes in plants can be done easily and does not require
sophisticated tools, so plants are a good alternative as bioassays.
Onion root is a research material
that has been widely used in the analysis of the toxicity of a pollutant. Onion
bulbs are easy to obtain and can be grown easily. Roots are part of plants that
are very useful in toxicity testing, because they are the first part to be
exposed to contaminants in the soil or in water. The onion root meristem
contains a high proportion of mitotic cells which are very important in
chromosome observation. Onion chromosomes are large, making it easier to
observe.
It is also very easy to make
chromosome preparations from the tip of the onion roots. Onions are rooted by
soaking in water, after the roots grow, they are transferred to a pollutant
solution for a certain period of time. Then the root tips are cut and immersed
in a fixative consisting of acetic acid and alcohol. After that, the root tips
were soaked in hydrochloric acid to soften the roots. The root tip was placed
on a slide then stained with aceto-orcein and covered with a cover slip, and
then pressed with the thumb so that the cells spread. Chromosomal damage is
then observed under a microscope.
Some types of chromosome
damage that are often observed in onions are fragmented chromosomes, sticky
chromosomes and chromosome bridges during anaphase and telophase. Several
studies have shown that onions are effective in detecting toxicity. Therefore
the toxicity test using the onion system is an important test tool in
environmental monitoring.
