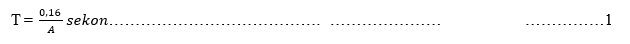Sabine and Eyring Mathematical Model for Determining the Buzzing Time of Space.
30/06/2020 Views : 395
Windarjoto
Sabine and Eyring Mathematical Model for
Determining the Buzzing Time of Space.
Author : Windarjoto
When someone sings in the bathroom, the sound becomes better, as if the person's breath is getting longer, but once the person sings the same song in the room to sleep, the sound becomes ugly. This happens because the sound in the room will not die if the source stops sounding. There is a room where the sound disappears after a long time, but there is also a room that sounds quickly disappear as happens in the sleeping room. The sound of someone singing in the bathroom becomes better, because the sound is reflected repeatedly by the walls of the room, so that the person's voice lives longer. In a room with a lot of absorbent material, the sound energy reflected is only a little, so the sound will die soon. Therefore, in acoustics there are two spaces, namely living space and dead space. The size of life or death of a room depends on the amount of absorbent material present in the space. Space with a lot of absorbent material is called dead space, whereas space with little absorbent material is called living space. The size of life or death of space is expressed as reverberation time. Some methods used to determine the reverberation time include: the Sabine and Eyring method.The relationship between reverberation time, room volume, and sound absorption has been studied by Sabine and followed by other researchers, such as Eyring. Equation of the reverberation time T according to Sabine:
Where: A = total absorption of space (m2 Sabine)
=
∑ Sn αn
Sn = surface area of the room that has absorption coefficient αn
If x represents the coefficient of absorption of air
per volume (sabine/m3),
Eyring assumes that space is really diffuse,
meaning that at every point in the space the level of sound intensity is the
same and energy is propagated in all directions the same, so the average
absorption coefficient is as follows
Where : S 1, S 2, ...... S n := luas permukaan bahan yang koefisien penyerapannya masing-masing α 1, α 2, ........ α n.
The reverberation time equation according to Eyring
The hum equation according to Sabine
Where :![]()
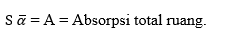
For this reason, with this description, equations 4 and 5 can be used in the design of space, meaning that the equation can be determined materials to be used on the surface of walls, floors or ceilings.